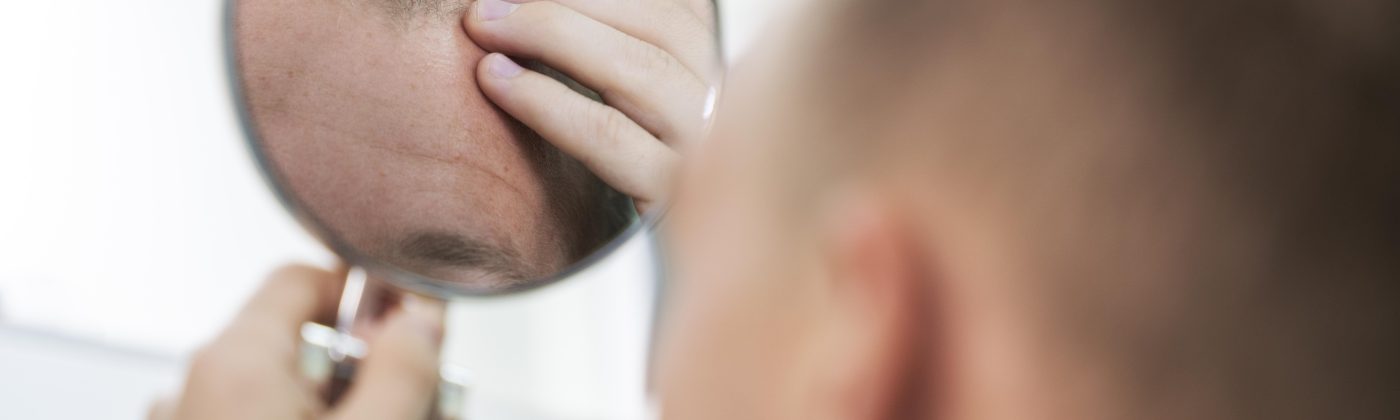
Post-Hair Transplant Complications and How to Prevent Them
Hair transplant surgery is a transformative procedure for individuals struggling with hair loss. While the prospect of regaining a full head of hair is exciting, it’s essential to acknowledge that like any surgical procedure, hair transplants carry risks of complications. Understanding these potential complications, along with strategies for prevention and management, is crucial for ensuring a successful outcome and a smooth recovery process.
Contents
Importance of Post-Hair Transplant Complications Awareness
Despite advancements in hair transplant techniques and technology, complications can still occur following the procedure. While complications are relatively rare, they can range from mild discomfort to more severe issues such as infection or graft failure. Recognizing the importance of post-hair transplant complications awareness is the first step in mitigating risks and ensuring patient safety.
Common Post-Hair Transplant Complications: A Comprehensive Overview
Several complications may arise following a hair transplant procedure, each with its unique causes, symptoms, and management strategies. These include:
1. Infection
- Infections can occur at the donor or recipient sites, leading to symptoms such as redness, swelling, and tenderness. Prompt treatment with antibiotics is essential to prevent the spread of infection and minimize complications.
2. Bleeding
- While some bleeding is normal immediately after the procedure, excessive bleeding may indicate underlying issues such as inadequate wound closure or clotting disorders. Proper wound care and monitoring can help manage bleeding effectively.
3. Swelling and Edema
- Swelling and edema are common side effects of hair transplant surgery, particularly in the forehead and eye area. Elevating the head, applying cold compresses, and avoiding strenuous activities can help alleviate swelling and discomfort.
4. Graft Failure
- Graft failure occurs when transplanted hair follicles do not survive or thrive in their new location. Factors such as poor blood supply, trauma, or incorrect placement can contribute to graft failure. Close monitoring and timely intervention are essential to salvage grafts and optimize outcomes.
5. Crusting and Itching
- Crusting and itching are normal parts of the healing process after a hair transplant. However, excessive scratching or picking can disrupt the healing process and increase the risk of infection. Gentle cleansing and moisturizing can help alleviate itching and promote proper healing.
6. Pain and Discomfort
- Some degree of pain and discomfort is expected after a hair transplant, particularly in the donor and recipient areas. Over-the-counter pain medications and cold compresses can provide relief, but patients should avoid aspirin-containing medications that may increase bleeding risk.
7. Scarring
- While modern hair transplant techniques aim to minimize scarring, some degree of scarring may still occur, particularly in individuals prone to keloid formation. Proper wound care and sun protection can help minimize the appearance of scars and promote optimal healing.
Strategies for Preventing and Managing Post-Hair Transplant Complications
Preventing and managing post-hair transplant complications require a multifaceted approach that involves pre-operative preparation, diligent post-operative care, and close communication between patients and surgeons. Key strategies include:
– Pre-operative Evaluation and Preparation
- Thoroughly evaluate patients’ medical history, including any underlying health conditions or medications that may increase the risk of complications.
- Educate patients about the potential risks and complications associated with hair transplant surgery and discuss realistic expectations.
– Optimal Surgical Technique and Patient Selection
- Employ meticulous surgical techniques to minimize trauma to the scalp and ensure proper graft placement.
- Select suitable candidates for hair transplant surgery based on factors such as age, hair loss pattern, and overall health.
– Post-operative Care and Monitoring
- Provide patients with detailed post-operative care instructions, including wound care, medication management, and activity restrictions.
- Schedule regular follow-up appointments to monitor patients’ progress, address any concerns or complications promptly, and adjust treatment as needed.
– Patient Education and Empowerment
- Educate patients about the importance of adherence to post-operative care instructions, including proper wound care, medication management, and lifestyle modifications.
- Encourage open communication and address any questions or concerns patients may have throughout the recovery process.
– Comprehensive Support and Resources
- Offer patients access to resources such as educational materials, support groups, and online forums where they can connect with others who have undergone hair transplant surgery.
- Provide ongoing support and guidance to help patients navigate the emotional and physical challenges of the recovery process.
Conclusion
While hair transplant surgery offers transformative results for individuals struggling with hair loss, it’s essential to acknowledge and address the potential risks and complications associated with the procedure. By understanding these risks, implementing preventive measures, and providing comprehensive support and resources, patients and surgeons can work together to minimize complications, optimize outcomes, and achieve successful hair transplant results.